RPA(Robotic Process Automation) is a software tool which can easily automate data transaction from one application to another as if it were operated by human via user interface. By using RPA, manual operations on information systems, Microsoft Office, browsers, etc. can be configured as "scenarios" and executed automatically on PC.
With RPA, you can automate a series of business processes that were previously performed by human such as;
(Refer to Figure1)
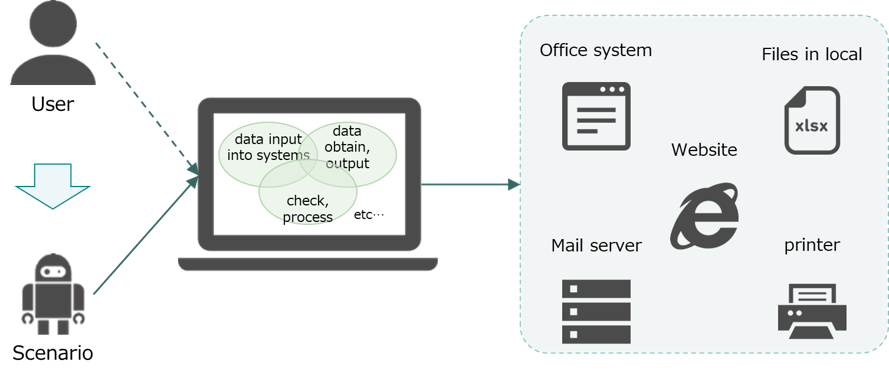
Figure1. Automate a series of business processes previously performed by humans
Recently, "labor shortage", "work style reform", and "improvement in productivity" have been important topics to be discussed. Therefore, RPA is expected to be able to automate small-lot and multi-product business processes that could not have been systemized for many years.
Around the 1990s, large-scale system investment such as introducing ERP began in Japan and business processes mainly in financial, accounting and personnel fields have been made more efficient than before. However, business processes which were not easy to be automated because of cost or security restrictions have not been systematized. Therefore, most of those business processes have still been handled by humans, using Excel, Access and so on. For example, even now, for the reports required for management accounting, a considerable amount of time and effort is required for a series of manual tasks such as outputting reports in Excel, processing data with Access, processing data with Excel again, and adjusting the appearance of reports. Even if the volume of each of these tasks is small, the total volume as a business process can be quite large by repeating it every day.
In order to make a decision to obtain additional investment for systematizing such business processes, it is necessary to continuously measure and accumulate the volume of each task and evaluate the return on investment. In the midst of daily work, employees force themselves to continue their work for many years, and it becomes natural to do so, and it is no longer considered a systemization target. In this way, a lot of manual work is left in the company without being systematized.
Leaving the manual work deepens the problem, as shown below. (Refer to Figure2)
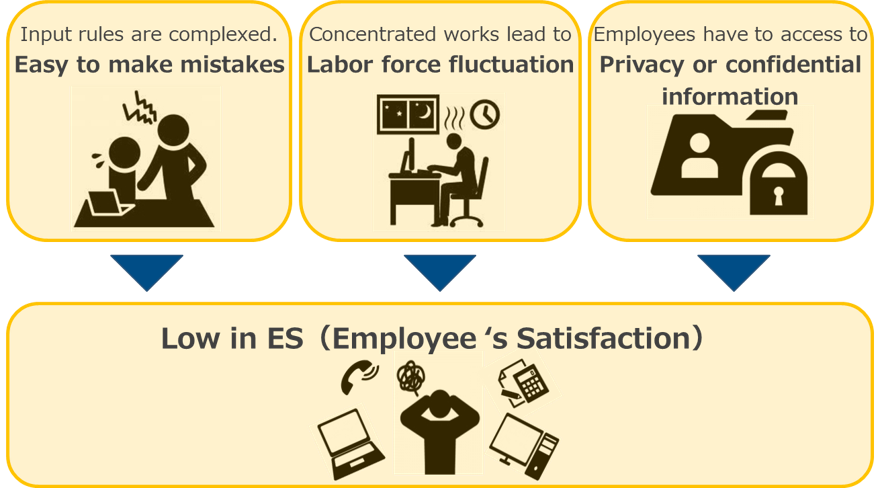
Figure2. Leaving the manual work deepens the problem
RPA is a tool that combines "UI (User Interface) recognition" and "Workflow" and enables the following:
※ As shown in Figure 3, there are three ways to recognize the operation target: "image recognition", "coordinate recognition", "structural analysis", or a combination thereof.
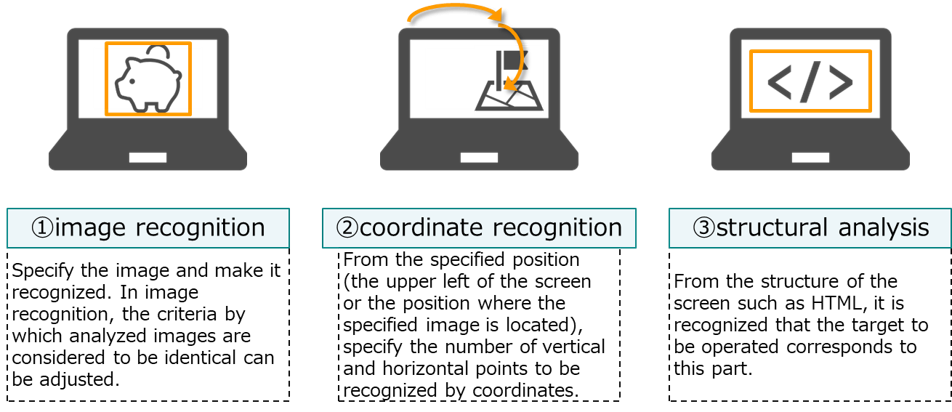
Figure3. Recognizing the operation target (information system or application)
The difference from conventional system linkage is that RPA realizes automation of operations centered on the user interface. Before RPA, system modification such as API and DB connection was required to link different systems. However, RPA can more easily achieve the same effect as inter-system cooperation via UI (user interface). (Figure 4) However, it is important to note that RPA cannot retain or share data like systems can do.
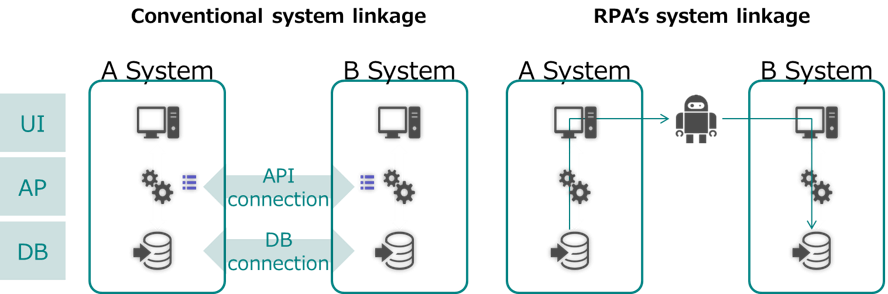
Figure4. Conventional system linkage and RPA's system linkage
RPA also looks similar to Excel's macro / VBA automation, but differs significantly in the following ways:
※Macro / VBA requires code description in a programming language (VBA). On the other hand, RPA can create scenarios using a GUI (Graphical User Interface), so it is intuitive and easy for beginners to use, requiring no special knowledge. Scenarios can be easily created by dragging and dropping the actions from a list of actions (called "library or node") prepared in advance in the tool (called "library or node"), and putting them into a flowchart (Figure 5).
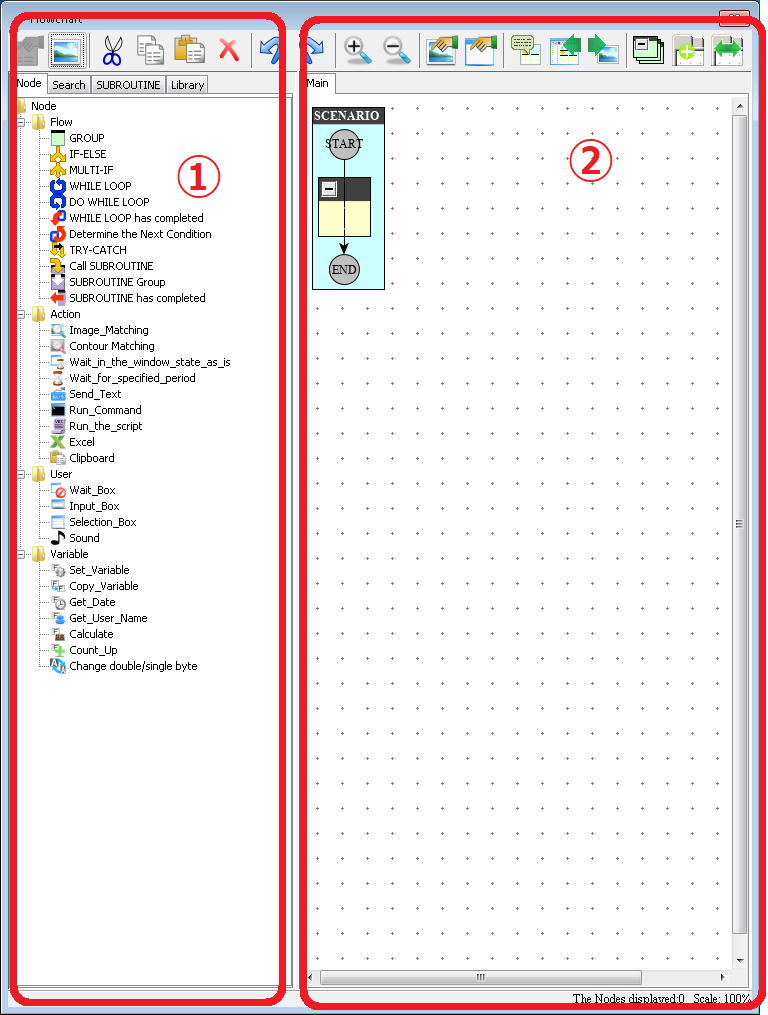
Figure5. Scenarios can be easily created by dragging and dropping
As described above, RPA is a tool that "substitutes operations performed on a PC" to the last, so RPA cannot do things that people cannot do in terms of operation and authority as follows.